Is CPU A Storage Device – A Complete Guide in 2024!
In the realm of computing, various components work in harmony to perform tasks and store data. Among these components, the Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often a subject of discussion and confusion.
No, the CPU is not a storage device. It processes data and temporarily stores information in its registers. For longer-term storage, data is sent to RAM or the hard drive. The CPU’s storage is lost when powered off.
This article aims to clarify “Is CPU A Storage Device“and the role of the CPU and distinguish it from storage devices.
What Is a CPU?
A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the main part of a computer that carries out instructions and processes data. It acts like the computer’s brain, making calculations and decisions to run programs and perform tasks.
What Is a CPU and Why Is It Important?
A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the main part of a computer that processes instructions and data. It’s important because it acts like the computer’s brain, allowing it to run programs and perform tasks quickly and efficiently.
What’s inside of a CPU?
Inside a CPU, you’ll find millions of tiny components like transistors, which handle calculations and data processing. It includes parts like the control unit, arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers, all working together to run programs efficiently.
What are the uses of the CPU?

- Data Processing: The CPU performs calculations and processes data, executing instructions from programs and applications.
- Running Applications: It enables the functioning of software applications, from simple word processors to complex video games and software.
- Multitasking: The CPU manages multiple tasks simultaneously, allowing users to run various applications at the same time.
- Operating System Management: It controls and executes the operating system, ensuring that hardware and software communicate effectively.
- Device Control: The CPU coordinates and controls peripheral devices like printers, keyboards, and mice, ensuring they work correctly with the computer.
- Executing Instructions: It interprets and executes program instructions, transforming them into actions like opening files or playing videos.
- Power Management: The CPU helps manage the computer’s power usage, optimizing performance and conserving energy when necessary.
- Security: It executes security protocols and encryption, protecting the computer from unauthorized access and malware.
- Artificial Intelligence: In AI applications, the CPU processes large amounts of data and performs complex calculations to support machine learning and data analysis.
- Networking: The CPU manages network connections, enabling data exchange between computers and internet access.
What’s the best CPU nowadays?
The best CPU today depends on your needs. For gaming, the Intel Core i9-13900K is top-rated. For heavy tasks like video editing, the AMD Ryzen 9 7950X is excellent. Both offer high performance and speed.
What are the uses of an old non-working CPU?
- Art Projects: Use it in sculptures, jewelry, or other creative art projects due to its intricate design.
- Keychains: Convert the CPU into a unique keychain by attaching a keyring.
- Educational Tool: Use it to teach electronics and computer hardware basics.
- Paperweight: Its solid structure makes it a stylish and geeky paperweight.
- Tech Decor: Incorporate it into tech-themed decorations or DIY projects.
- Recycling: Extract valuable metals like gold, silver, and copper through specialized recycling processes.
- Donations: Donate to schools or tech clubs for educational purposes or disassembly practice.
- Conversation Piece: Display it as a conversation starter or collectible item.
- Upcycling Projects: Integrate it into larger upcycling projects involving other old electronics.
- Memory Keepsake: Keep it as a memento if it was part of a significant computer or project.
What are the different parts of the CPU (CPU, ALU, MU)?
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a part of the CPU that performs mathematical calculations (like addition and subtraction) and logical operations (like comparing values). It is crucial for executing instructions and processing data.
Memory Unit (MU):
The Memory Unit (MU) of the CPU is responsible for storing and managing data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. It includes components like registers and cache memory that temporarily hold data for fast retrieval.
Control Unit (CU):
The Control Unit (CU) directs the CPU’s operations by fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, and then executing them. It manages the flow of data between the CPU and other components, ensuring that tasks are performed in the correct order.
What are the full forms of MU, CU, and ALU in computers?
Memory Unit (MU):
The Memory Unit (MU) is a part of the CPU that stores data and instructions temporarily. It includes registers and cache that help the CPU quickly access the information needed for processing tasks.
Control Unit (CU):
The Control Unit (CU) directs and manages the operations of the CPU. It fetches, decodes, and executes instructions, coordinating the flow of data between the CPU and other computer components.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) performs all mathematical calculations and logical operations within the CPU. It handles tasks like addition, subtraction, and comparisons, enabling the CPU to process and execute instructions.
What does an ALU inside a CPU do?
The ALU inside a CPU performs mathematical calculations like addition and subtraction, as well as logical operations like comparing values. It processes these tasks to help the CPU execute instructions and run programs efficiently.
What is not present inside the CPU box?
Inside the CPU box, you won’t find components like the hard drive, RAM, or graphics card. These parts are separate and connected to the CPU, but they are not physically inside the CPU box itself.
What does a CPU consist the least of?
A CPU consists of very few physical parts, primarily the core processor units like the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and Control Unit (CU). It has minimal physical components compared to other computer parts like RAM or storage drives.
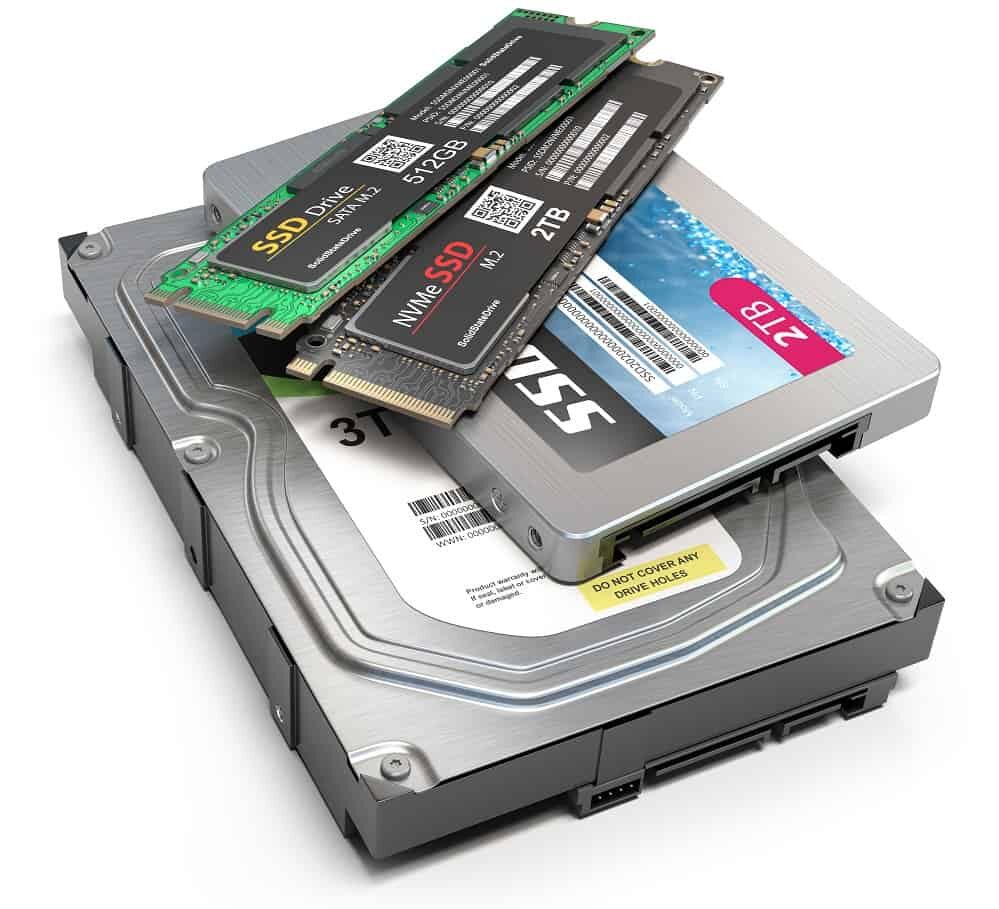
What is a Storage Device?
A storage device is a hardware component used to save and keep data. Examples include hard drives, SSDs, and USB flash drives. These devices store files, programs, and system data so they can be accessed later.
3 types of storage devices!
Hard Drive:
A hard drive is a storage device that uses spinning disks and magnetic heads to store and retrieve large amounts of data. It’s commonly used for long-term storage of files, programs, and the operating system.
SSD (Solid State Drive):
An SSD, or Solid State Drive, is a storage device that uses flash memory to store data. It’s faster and more reliable than a hard drive because it has no moving parts, which improves the speed of accessing and writing data.
USB Flash Drive:
A USB flash drive is a portable storage device that connects to a computer via a USB port. It uses flash memory to store data, making it easy to transfer files between computers and carry data on the go.
Storage devices of the computer!

Storage devices of a computer include hard drives for large data storage, SSDs for faster access, and USB flash drives for portable file transfers. These devices keep files and programs so they can be accessed and used later.
Is the CPU a storage device?
No, the CPU is not a storage device. It processes data and executes instructions. Storage devices, like hard drives or SSDs, are used to save and keep data long-term, while the CPU handles calculations and tasks.
Is a CPU a processing device?
Yes, a CPU is a processing device. It carries out instructions and performs calculations to run programs and manage tasks. It acts as the brain of the computer, handling data and controlling other components.
Read more: Is CPU Hardware or Software – Ultimate Guide – 2024!
Is the motherboard a storage device?
No, the motherboard is not a storage device. It connects and allows communication between the CPU, memory, and other components. Storage devices like hard drives or SSDs are used to save and keep data.
Is RAM a storage device?
No, RAM is not a storage device. It is a type of memory that temporarily holds data and programs while the computer is running. Storage devices, like hard drives or SSDs, keep data long-term even when the computer is off.
How is RAM different from storage?

Purpose:
- RAM: Temporarily holds data and programs that are currently in use by the CPU for quick access.
- Storage: Permanently saves data and files for long-term use, even when the computer is turned off.
Volatility:
- RAM: Volatile memory, meaning it loses all data when the power is turned off.
- Storage: Non-volatile memory, retaining data even without power.
Speed:
- RAM: Faster access and read/write speeds, which improves the performance of running applications.
- Storage: Slower access speeds compared to RAM, but designed for long-term data storage.
Capacity:
- RAM: Typically has a smaller capacity compared to storage devices, ranging from a few gigabytes to dozens of gigabytes.
- Storage: Generally has a larger capacity, ranging from hundreds of gigabytes to several terabytes.
Functionality:
- RAM: Provides temporary workspace for the CPU, helping with multitasking and fast processing.
- Storage: Stores operating systems, applications, and user files for long-term access.
What is the difference between RAM and SSD storage?
RAM provides temporary, fast access to data currently in use by the CPU, while SSD storage offers long-term, slower access to data and files. RAM loses its data when the computer is turned off, but SSDs keep data even without power.
Do RAM chips last longer than SSD storage systems?
No, RAM chips do not last longer than SSD storage systems. SSDs are designed for long-term data storage and can last for several years, while RAM is more prone to wear and typically lasts a shorter time.
What is the difference between RAM and disk storage?
RAM (Random Access Memory):
- Purpose: Temporarily holds data and programs that the CPU is currently using.
- Volatility: Volatile memory, which means it loses all data when the power is turned off.
- Speed: Provides fast access to data for quick processing and multitasking.
- Capacity: Generally has a smaller capacity compared to disk storage, ranging from a few gigabytes to dozens of gigabytes.
- Functionality: Enhances computer performance by allowing quick access to active tasks and data.
Disk Storage (Hard Drives and SSDs):
- Purpose: Stores data and files permanently for long-term use, even when the computer is off.
- Volatility: Non-volatile memory, retaining data without power.
- Speed: Slower access speeds compared to RAM, though SSDs are faster than traditional hard drives.
- Capacity: Typically has a larger capacity, ranging from hundreds of gigabytes to several terabytes.
- Functionality: Provides long-term storage for the operating system, applications, and user files.
Why is RAM faster than disk storage?
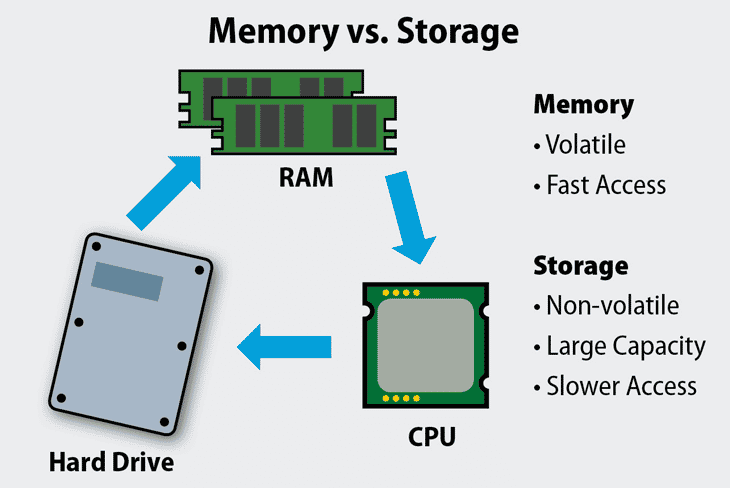
RAM is faster than disk storage because it uses electronic circuits to quickly access and process data, while disk storage relies on mechanical parts (in hard drives) or slower flash memory (in SSDs), which makes it slower in comparison.
Is monitoring a storage device?
No, monitoring is not a storage device. Monitoring refers to tracking and checking the performance or status of computer systems and devices. Storage devices, like hard drives and SSDs, are used to save and keep data.
What is the difference between CPU RAM and a storage device?
CPU:
- Purpose: Executes instructions and processes data.
- Function: Acts as the computer’s brain, handling calculations and tasks.
RAM (Random Access Memory):
- Purpose: Temporarily holds data and programs for quick access.
- Function: Provides fast, temporary memory that the CPU uses while the computer is running.
Storage Device:
- Purpose: Permanently stores data and files.
- Function: Saves information long-term, even when the computer is turned off. Examples include hard drives and SSDs.
Understanding CPU, RAM, HDD/SSD!
The CPU processes data and runs programs, RAM provides fast temporary memory for active tasks, and HDD/SSD are storage devices that save files and data long-term. The CPU handles tasks, RAM speeds up processing, and HDD/SSD stores information permanently.
know that it has to READ 0s and 1s from a storage device!
The computer must read 0s and 1s from a storage device to access data. These 0s and 1s represent information stored in binary code, which the computer processes to run programs and manage files.
How do I clean my CPU from the insides?
To clean your CPU from the inside, turn off the computer, unplug it, and carefully use compressed air to remove dust from the CPU and its cooling fan. Avoid using liquids or touching components directly to prevent damage.
Read more: Is 100°C Too Hot for CPU – Complete Guide – 2024!
What parts/components are inside an Intel CPU?
Inside an Intel CPU, you’ll find the core processor units, such as the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit (CU), and various transistors. These components work together to process instructions and manage data.
What is the temporary storage location inside the CPU?
The temporary storage location inside the CPU is called the cache. It holds data and instructions that the CPU is currently using for quick access, speeding up processing by reducing the need to fetch data from slower memory.
FAQS:
1. What is a CPU?
A CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the brain of a computer that executes instructions and processes data. It handles calculations and runs programs to make the computer function.
2. What is a storage device?
A storage device is hardware used to save and keep data, such as files and programs. Examples include hard drives, SSDs, and USB flash drives.
3. Is CPU or RAM more important?
Both CPU and RAM are crucial for a computer. The CPU handles processing tasks, while RAM provides quick access to active data and programs, so both are important for performance.
4. What is the role of a CPU concerning storage devices?
The CPU processes data and sends instructions to storage devices. It reads from and writes to storage to access and save files.
5. Why is it important to differentiate between a CPU and a storage device?
Differentiating between a CPU and a storage device is important because the CPU processes data, while storage devices save and retain data. Understanding their roles helps in choosing and managing computer components effectively.
6. Is CPU a storage device or not?
No, the CPU is not a storage device. It processes data and performs calculations, while storage devices keep data for long-term use.
7. Is the CPU a valid storage device?
No, the CPU is not a valid storage device. It processes data, but does not store information long-term; that function is performed by devices like hard drives or SSDs.
Conclusion:
The CPU is not a storage device but a processing unit that performs calculations and runs programs. It temporarily holds data in its cache but relies on RAM and storage devices like hard drives or SSDs for long-term data storage. Understanding the roles of each component helps clarify how they work together to make a computer function effectively